
|
eValid™ -- The Web Quality Suite
Browser-Based Client-Side Functional Testing and Validation
Page Timing/Tuning Transaction Monitoring.
WebSite Spidering & Analysis and Realistic Server Loading.
|
|
eValid -- Structural Testing Commands
eValid Home
Introduction
Below is a summary of the primitive commands that
apply in DOM manipulation scripts/programs.
(Here "primitive" is meant in the mathematical sense that implies that
these commands are ALL that you need to do ANYthing, making them "universal".)
All of these commands act on the
internally maintained "sourceIndex" and "elementValue" string values.
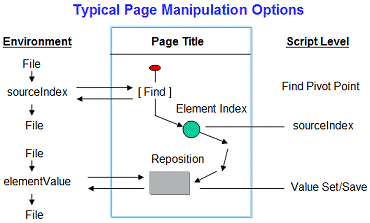
These commands are the ones used in the
Manual Script Creation Process, as shown in this diagram:
Review of Basic Facts
This section can be skipped if you already know these facts.
- Each web page has a Document Object Model (DOM) structure.
- In the DOM the page is composed of individual elements -- there could be hundreds or even thousands of them.
- The page could be divided up into frames, which can be named or not named, and can be nested (often very deeply).
- Each frame has a unique identifying sequence, called the FramePath
- Each DOM element in each frame has a unique index, its "sourceIndex," starting at sourceIndex = 0 and increasing
as you move down the page.
- Associated with any DOM element is a set of attributes (sometimes also called properties).
Any attribute (property) can have a value, called the "elementValue", which is always a character string.
- Typical functional testing sequences involve a variety of manipulations of the sourceIndex and
particular attribute (property) elementValue strings.
Processing Steps
Here are the main processing steps involved in working with the DOM:
- Manipulating Values for "sourceIndex" and "elementValue"
Extracting, inserting, saving and recovering current values for the
sourceIndex or elementValue strings:
- IndexSet
- IndexRead
- ValueSet
- ValueRead
- ValuePutElement
- ValueGetElement
- Pointing "sourceIndex" At Something (Localizing)
From the current location, reposition the sourceIndex to the location
of some particular property.
- IndexMove
- IndexFindElement (2 variations)
- IndexFindElementEX (multiple, chained variations)
- Modifying (Extracting, Inserting) Attribute Values
Once a sourceIndex on the page is identified, you can take a variety of
actions (depending on what type of object it is), or you can manipulate
specific values of individual attributes (properties) of that sourceIndex.
- IndexSave
- IndexSaveObjProperty
- IndexInputValue
- ValueSave
- ValueGetElement, ValuePutElement
- Acting On The Object To Which The Current "sourceIndex" Points
Take a user-like action on the current sourceIndex.
- IndexElementClick
- IndexElementMouse[Down|Out|Over|Up]
- IndexFollowLink
- IndexSubmitClick
- IndexElementEvent
- Synchronizing (Waiting For Something) Before Continuing Playback
- SyncOnText
- SyncOnElementProperty
- SyncOnSelectedObjProperty
- SyncNotOnElementProperty
- SyncNotOnSelectedObjProperty
- Validating Results Within A Page
- IndexValidateObjProperty
- ValidateSelectedObjProperty
- ValidateSelectedText
- CompareStrings
Other Commands
There are many other eValid commands available that do NOT
pivot on the
internally maintained "sourceIndex" and "elementValue" string values.
These commands use the current DOM idx and/or the current idx's ID
value as pivots.
